Roche has shown interest in RNA Editing through its 2021 partnership with Shape Therapeutics. The goal of this partnership was to use Shape’s AAV-delivered, DNA-directed RNA editing nucleic acids for neuroscience and rare disease applications.
Readers of
this blog will know that I have not been a great fan of DNA-directed approaches
to ADAR editing, not least because the expressed editing RNAs are unmodified. This means that they do not benefit from chemistry to optimize efficacy. In terms
of specificity, the simple, but very effective strategy of modifying the base opposite non-target adenosines (e.g. 2’-O-methyl) to abolish off-target editing is not available to DNA-directed RNA editing.
To compensate the efficacy disadvantage, the concomitant gene therapy-directed overexpression of ADAR
enzymes has been attempted. Unfortunately, this is a no-go since it causes extensive genome-wide off-targeting.
It therefore comes as no surprise that Roche has also been evaluating synthetic
editing oligonucleotides as revealed earlier this month in patent publication WO2023/052317A1. This patent application addresses CAG/polyglutamine
repeat expansion diseases such as Huntington’s disease, but also other neurodegenerative polyGln diseases including a number of the spinal cerebellar ataxias. Since the number
of polyGln repeats critically determines whether a person will manifest the
disease and is correlated with protein aggregation, disrupting stretches of
CAG-encoded uncharged glutamines with even a few positively charged, CGG-encoded
arginines may stop the pathogenic process and is thus a highly attractive
therapeutic hypothesis.
Beyond CAG triplett expansion diseases, similar logic may apply to diseases caused by repeat expansions in non-coding regions- as long as the repeat contains an ‘A’ such as in Friedreich’s
ataxia (frataxin GAA repeat in intron 1). Regardless
of the specific disease-causing mechanism, disrupting the repeat is likely to be
beneficial.
While
attractive in theory, I had been wondering how easy it actually would be to
target these repeats by ADAR editing as the target sequence is quite unusual in its repetitiveness which may result in impenetrable higher-order structures. The use of repetitive oligonucleotides as
therapeutic agents is also unusual because of potential structural and
manufacturing issues. Finally, once one
of the target adenosines has been converted to an inosine, the target mRNA
sequence is altered (=mismatch) and consequently may become a weaker target site.
On the
other hand, long repeats may turn out to be excellent targets in that they
provide for a high local concentration of target sequence.
Actual
data
Unfortunately,
conducting casual molecular biology experiments in the basement of private homes is frowned upon in
Germany and fraught with legal risks (this has to change), so it’s nice that Roche
has actually conducted initial tissue culture experiments to find out about the
practicality of the approach.
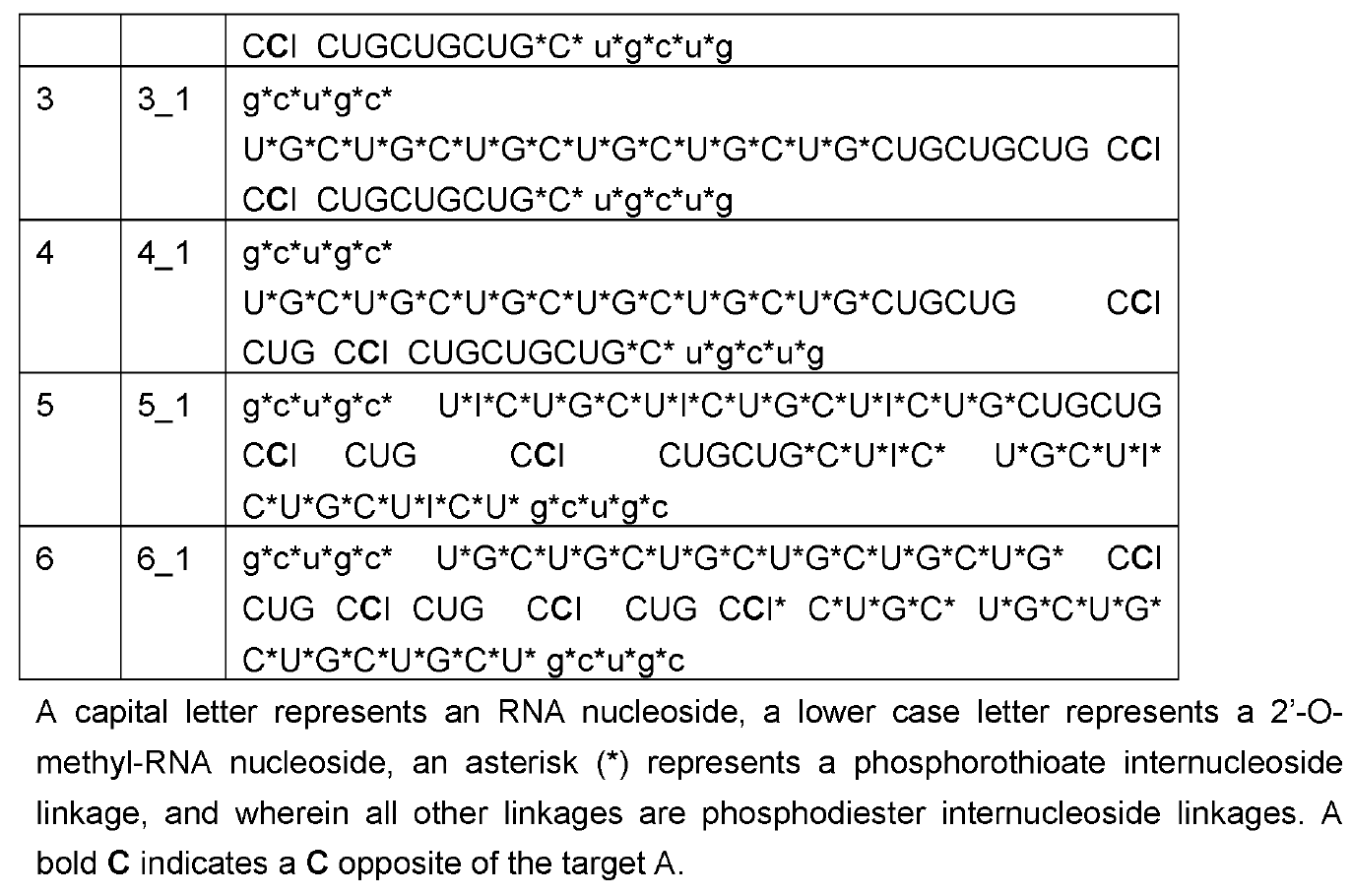
Employing ~50-60nt long CUG repeats (the complement of CAG), their editing oligonucleotides were above the typical length of ~30nt as now generally practiced by the leading RNA Editing companies ProQR and Wave Life Sciences. These were transfected into HeLa cells expressing ATXN3 mRNA with 21-22 repeat CAGs all in the apparent absence of ADAR overexpression.
The
oligonucleotides were modified with 2’-o-methyl only in the 5 nucleotides on
the 5’ and 3’ ends each; phosphorothioation of the backbone was also practiced at the wings of the oligos, but extended further into
the center than the 2'-o-methyls. The central part
consisted of pure RNA.
An orphan C was placed towards the 3’ end of the targeting oligo. This creates a mismatch to the target A as is commonly practiced in the field. Interestingly, an inosine follows 3’ of the orphan C and this is also practiced by some other companies as e.g. evidenced in last year’s high-profile paper on long-lived and potent ADAR editing in non-human primates by Wave Life Sciences in Nature Biotech.
Remarkably,
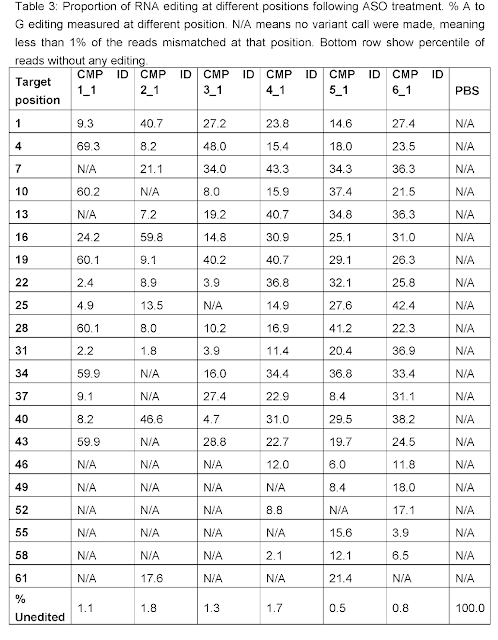
robust 20-50% AàI
conversions were seen for many As in the ATXN3 CAG repeat with more pronounced editing
towards the 5’ end of the repeat region consistent with the 3’ placement of the
orphan C in the targeting oligonucleotide.
Moreover, less than 2% of the ATXN3 mRNAs was unmodified for each editing
oligo. If you consider that a
huntingtin allele with say 33 CAG repeats does not result in Huntington’s
disease, but one with 37 repeats typically does, you can imagine the impact
that just a single or two successful editing events should have on
pathogenicity of the resulting protein.
This experiment thus is an important de-risking step for RNA Editing in repeat expansion diseases and should whet the appetite of Roche which is already heavily invested in oligonucleotide therapeutics for Huntington’s through its collaboration with Ionis Pharmaceuticals (RNaseH mechanism), including research on improving the convenience and efficacy of intrathecal oligo administration.
As an
investor in ProQR I was, of course, pleased to see that when discussing the
prior art of ADAR editing in general, all 5 patent applications cited by Roche
referred to ones controlled by ProQR.